一、前言
上篇在介绍 Spring Boot 集成 Dubbo 时,埋下了有关返回值格式的一个小小伏笔。本篇将主要介绍一种常用的返回值格式以及详细说明。
二、Dubbo 接口统一返回值格式
我们在应用中经常会涉及到 server 和 client 的交互,目前比较流行的是基于 json 格式的数据交互。但是 json 只是消息的格式,其中的内容还需要我们自行设计。不管是 HTTP 接口还是 RPC 接口保持返回值格式统一很重要,这将大大降低 client 的开发成本。
2.1 定义返回值四要素
- boolean success ;是否成功。
- T data ;成功时具体返回值,失败时为 null 。
- Integer code ;成功时返回 0 ,失败时返回具体错误码。
- String message ;成功时返回 null ,失败时返回具体错误消息。
2.2 定义错误码
为了兼容多种类型的错误码,可以通过声明接口的方式解决,再由具体的业务错误码类实现该接口。
① 首先在 demo-common 层的 com.example.demo.common 包中添加 error 目录并新建 ServiceErrors 错误码接口类。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22package com.example.demo.common.error;
/**
* @author linjian
* @date 2019/3/14
*/
public interface ServiceErrors {
/**
* 获取错误码
*
* @return Integer
*/
Integer getCode();
/**
* 获取错误信息
*
* @return String
*/
String getMessage();
}
② 其次再定义一个业务错误码枚举类实现上述接口类。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32package com.example.demo.common.error;
/**
* @author linjian
* @date 2019/3/14
*/
public enum DemoErrors implements ServiceErrors {
/**
* 错误码
*/
SYSTEM_ERROR(10000, "系统错误"),
PARAM_ERROR(10001, "参数错误"),
;
private Integer code;
private String message;
DemoErrors(Integer code, String message) {
this.code = code;
this.message = message;
}
public Integer getCode() {
return code;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
}
2.3 定义 Result 返回包装类
继续在 demo-common 层的 com.example.demo.common 包中添加 entity 目录并新建 Result 返回包装类。其中提供了 wrapSuccessfulResult 及 wrapErrorResult 方法用于接口调用成功或失败时的返回。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119package com.example.demo.common.entity;
import com.example.demo.common.error.ServiceErrors;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* @author linjian
* @date 2019/3/14
*/
public class Result<T> implements Serializable {
private T data;
private boolean success;
private Integer code;
private String message;
public Result() {
}
public static <T> Result<T> wrapSuccessfulResult(T data) {
Result<T> result = new Result<T>();
result.data = data;
result.success = true;
result.code = 0;
return result;
}
public static <T> Result<T> wrapSuccessfulResult(String message, T data) {
Result<T> result = new Result<T>();
result.data = data;
result.success = true;
result.code = 0;
result.message = message;
return result;
}
public static <T> Result<T> wrapErrorResult(ServiceErrors error) {
Result<T> result = new Result<T>();
result.success = false;
result.code = error.getCode();
result.message = error.getMessage();
return result;
}
public static <T> Result<T> wrapErrorResult(ServiceErrors error, Object... extendMsg) {
Result<T> result = new Result<T>();
result.success = false;
result.code = error.getCode();
result.message = String.format(error.getMessage(), extendMsg);
return result;
}
public static <T> Result<T> wrapErrorResult(Integer code, String message) {
Result<T> result = new Result<T>();
result.success = false;
result.code = code;
result.message = message;
return result;
}
public T getData() {
return this.data;
}
public Result<T> setData(T data) {
this.data = data;
return this;
}
public boolean isSuccess() {
return this.success;
}
public Result<T> setSuccess(boolean success) {
this.success = success;
return this;
}
public Integer getCode() {
return this.code;
}
public Result<T> setCode(Integer code) {
this.code = code;
return this;
}
public String getMessage() {
return this.message;
}
public Result<T> setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
return this;
}
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("{");
sb.append("success=");
sb.append(this.success);
sb.append(",");
sb.append("code=");
sb.append(this.code);
sb.append(",");
sb.append("message=");
sb.append(this.message);
sb.append(",");
sb.append("data=");
sb.append(this.data);
sb.append("}");
return sb.toString();
}
}
2.4 定义业务异常类
在 demo-biz 层的 com.example.demo.biz 包中添加 exception 目录并新建 BizException 异常类。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26package com.example.demo.biz.exception;
import com.example.demo.common.error.ServiceErrors;
/**
* @author linjian
* @date 2019/3/15
*/
public class BizException extends RuntimeException {
private final Integer code;
public BizException(ServiceErrors errors) {
super(errors.getMessage());
this.code = errors.getCode();
}
public BizException(Integer code, String message) {
super(message);
this.code = code;
}
public Integer getCode() {
return this.code;
}
}
2.5 定义异常处理切面
前面的准备工作做好之后,接下来才是真正的统一格式处理。不管是 HTTP 接口 还是 RPC 接口,在处理业务逻辑时,都可以通过抛出业务异常,再由 Spring AOP 切面捕捉并封装返回值,从而达到对外接口返回值格式统一的目的。
① 首先在 demo-web 层的 pom 文件中引入 Spring AOP 的依赖包。该包已经集成在 Spring Boot 提供的父工程中,这里直接引入即可。1
2
3
4<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
② 其次在 demo-web 层的 com.example.demo.web 包中添加 aspect 目录并新建 DubboServiceAspect 切面类。通过「拦截器」及「反射」实现将业务异常封装为 Result 返回。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55package com.example.demo.web.aspect;
import com.example.demo.biz.exception.BizException;
import com.example.demo.common.entity.Result;
import com.example.demo.common.error.DemoErrors;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @author linjian
* @date 2019/3/14
*/
4j
public class DubboServiceAspect implements MethodInterceptor {
public Object invoke(final MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable {
try {
return methodInvocation.proceed();
} catch (BizException e) {
log.error("BizException", e);
return exceptionProcessor(methodInvocation, e);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Exception:", e);
return exceptionProcessor(methodInvocation, e);
}
}
private Object exceptionProcessor(MethodInvocation methodInvocation, Exception e) {
Object[] args = methodInvocation.getArguments();
Method method = methodInvocation.getMethod();
String methodName = method.getDeclaringClass().getName() + "." + method.getName();
log.error("dubbo服务[method=" + methodName + "] params=" + Arrays.toString(args) + "异常:", e);
Class<?> clazz = method.getReturnType();
if (clazz.equals(Result.class)) {
Result result = new Result();
result.setSuccess(false);
if (e instanceof BizException) {
result.setCode(((BizException) e).getCode());
result.setMessage(e.getMessage());
} else {
result.setCode(DemoErrors.SYSTEM_ERROR.getCode());
result.setMessage(DemoErrors.SYSTEM_ERROR.getMessage());
}
return result;
}
return null;
}
}
③ 定义处理类之后再通过 Spring XML 的形式定义切面,在 demo-web 层的 resources 目录中新建 spring-aop.xml 文件,在其中定义 Dubbo 接口的切面。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="dubboRemoteServiceAspect"
expression="execution(* com.example.demo.remote.service.*.*(..))"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="dubboServiceAspect" pointcut-ref="remoteServiceAspect"/>
</aop:config>
</beans>
④ 继续在 demo-web 层的 resources 目录中,再新建 application-context.xml 文件统一管理所有 Spring XML 配置文件,现在先往其中导入 spring-aop.xml 文件。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<import resource="classpath:spring-aop.xml"/>
</beans>
⑤ 最后在 DemoWebApplication 入口类中通过 @ImportResource 注解导入 Spring 的 XML 配置文件。1
({"classpath:application-context.xml"})
此时处理异常的切面已经配置完毕,接下来通过修改之前定义的 RpcDemoService.test 方法测试切面是否有效。
2.6 切面测试
① 首先将 RpcDemoService.test 方法的返回结果用 Result 包装。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20package com.example.demo.remote.service;
import com.example.demo.common.entity.Result;
import com.example.demo.remote.model.param.DemoParam;
import com.example.demo.remote.model.result.DemoDTO;
/**
* @author linjian
* @date 2019/3/15
*/
public interface RpcDemoService {
/**
* Dubbo 接口测试
*
* @param param DemoParam
* @return DemoDTO
*/
Result<DemoDTO> test(DemoParam param);
}
1 | package com.example.demo.biz.service.impl.remote; |
② 再修改 DemoService.test 方法的内部逻辑,查询数据库后先判断是否有数据,没有的话抛出一个业务异常。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33package com.example.demo.biz.service.impl;
import com.example.demo.biz.exception.BizException;
import com.example.demo.biz.service.DemoService;
import com.example.demo.common.error.DemoErrors;
import com.example.demo.dao.entity.UserDO;
import com.example.demo.dao.mapper.business.UserMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* @author linjian
* @date 2019/1/15
*/
public class DemoServiceImpl implements DemoService {
private UserMapper userMapper;
public String test(Integer id) {
Assert.notNull(id, "id不能为空");
UserDO user = userMapper.selectById(id);
if (Objects.isNull(user)) {
throw new BizException(DemoErrors.USER_IS_NOT_EXIST);
}
return user.toString();
}
}
③ 然后 cd 到 demo-remote 目录,执行 mvn deploy 命令重新打包。此时服务提供者的调整工作已结束,接下来通过测试项目看效果。
④ 来到测试项目,调整中的 TestController.test 方法,增加 id 传参。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30package com.yibao.dawn.web.controller;
import com.alibaba.dubbo.config.annotation.Reference;
import com.example.demo.common.entity.Result;
import com.example.demo.remote.model.param.DemoParam;
import com.example.demo.remote.model.result.DemoDTO;
import com.example.demo.remote.service.RpcDemoService;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author linjian
* @date 2019/3/7
*/
("test")
public class TestController {
(version = "1.0.0.dev")
private RpcDemoService rpcDemoService;
("dubbo")
public Result<DemoDTO> test(@RequestParam("id") Integer id) {
DemoParam param = new DemoParam();
param.setId(id);
return rpcDemoService.test(param);
}
}
⑤ 测试在传参 id = 1 及 id = 2 的情况下,分别有如下返回结果: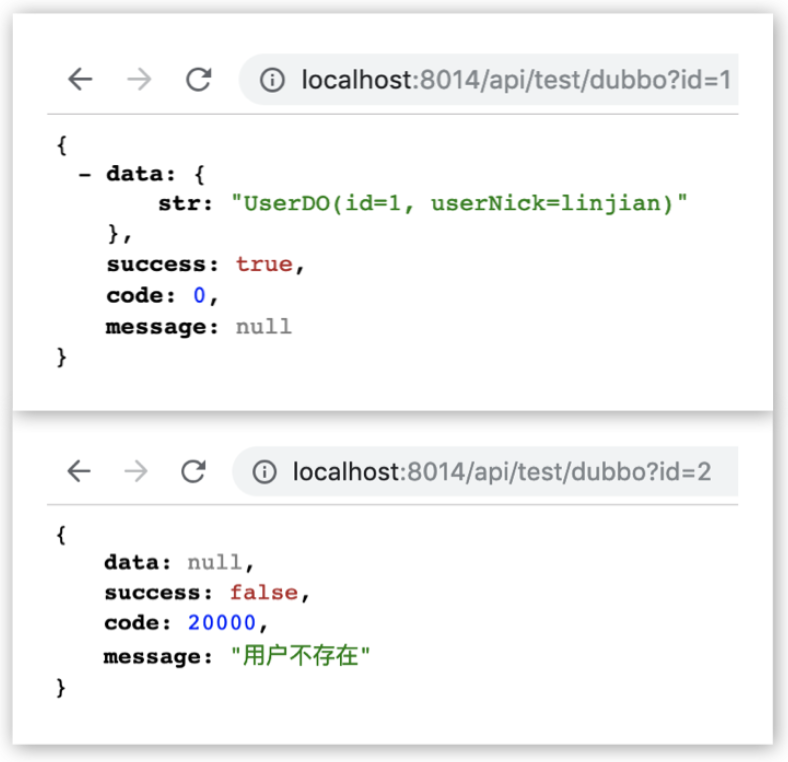
因为此时数据库中只有 id = 1 的一条数据,当传参 id = 2 时就触发了 DemoErrors.USER_IS_NOT_EXIST 的业务异常。
三、HTTP 接口统一返回值格式
3.1 定义切面处理类
1 | package com.example.demo.web.aspect; |
3.2 定义切面
在 spring-aop.xml 文件中追加一个切面定义。1
2
3
4
5
6<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="resultControllerAspect"
expression="@within(org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController)
and execution(com.example.demo.common.entity.Result *.*(..))"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="httpServiceAspect" pointcut-ref="resultControllerAspect"/>
</aop:config>
四、结语
至此接口统一返回值格式的方法介绍完毕,如果公司内部项目多了,可以将一些公用的组件提取出来单独作为一个项目打成二方包供其他项目依赖,保持内部项目的统一。
注:相关代码已同步至 GitHub